Sometimes substances are required to be move against the Concentration Gradient, or faster than they would by Passive Transport. In these cases, Active Processes are used, which require energy.
 There are many occasions when cells need to take in substances which are only present in small quantities around them.
There are many occasions when cells need to take in substances which are only present in small quantities around them.
E.g. root hair cells in plants take in nitrate ions from the soil. Their concentration are often higher inside the root hair cell than in the soil, so the diffusion gradient is from the root hair à the soil. Despite this, the root hair cells still can take nitrate ions in, by active transport.
The importance of active transport: energy-consuming process by which substances are transported against a concentration gradient, e.g. ion uptake by root hairs and glucose uptake by epithelial cells of villi.
- direction of movement (down or up a gradient)
- use of energy for movement
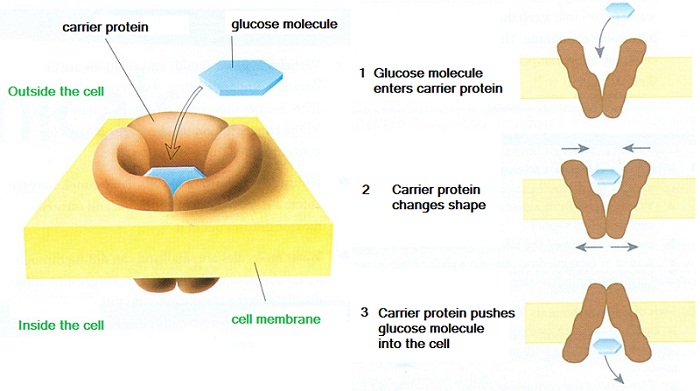
The active transport is carried out by ‘carrier proteins’ in the membrane, which bind to the solute molecule, change shape and carry the molecule across the membrane.
Try this
Figure above shows root hair cells.
b)Explain why respiration rates may increase in root hair cells during the uptake of mineral ions [1 mark]- Explain how the presence of root hair cells on roots enables the efficient absorption of water and minerals. [2 marks]
- Root hair cells can absorb mineral ions by diffusion and active transport.
Answers
1. - Large number of root hair cells give a large surface area to the root.
- Mitochondria are present to provide energy for active transport.
2. a) active transport is absorption of a substance into a cell or across a membrane
- against (up) a concentration gradient.
- using energy




0 Response to "Active transport"
Post a Comment